About IAI
Immersive Artificial Intelligence (IAI) provides a holistic view of different AI techniques that aims to enrich and take advantage of immersive human experiences in partially or fully virtual environments.
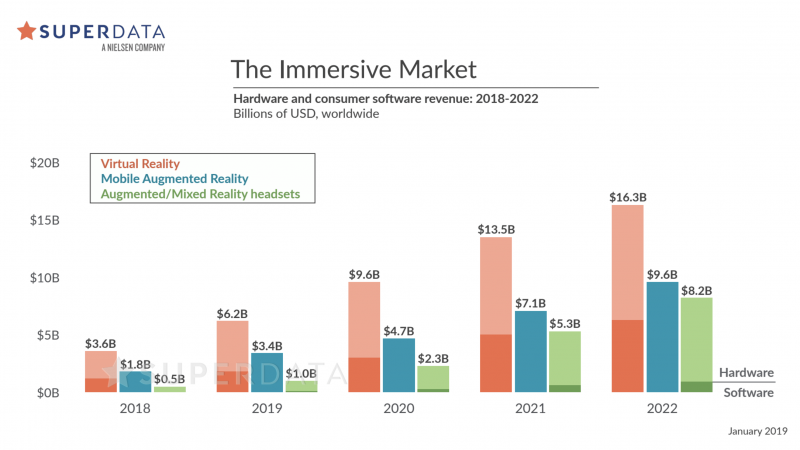
In this sense, the use of classical techniques to enhance the immersive user experience, the use of new techniques to assist decision-making in artificial environments or to analyse data derived from this experience, and the new capabilities in computation and artificial immersion, make IAI one of the most promising approaches both from an academic and professional point of view in Virtual Reality (VR). While the global market for VR is expected to grow to $22.37 billions by 2025, the closely related marked of the “metaverse” is calculated to reach $49 billions in 2020 and grows at a rate of 40% a year in successive years, according to a recent article.
The combination of optimised behaviours by means of Machine Learning (ML) techniques with Multiagent Systems (MAS) environments and classical argumentation and decision-making systems opens up a very productive research path given the flexibility it provides along with an enriched and realistic vision for the type of immersive experiences that are pursued in this project. The uses of this AI cover the full range of applications associated with the new horizons of AI: video games, robotics (autonomous and assisted), intelligent environments, human behaviour analysis, simulation and training of educational and work environments, human-agent interactions, health systems, Building Information Modelling (BIM) analysis, cultural studies, urban and smart-cities development, autonomous vehicles, etc.
In recent years, there has been an explosion in the development and use of immersive experience applications. Although at the beginning its uses were mainly oriented to the military context, the technological development of embedded systems with sufficient computational capacity and the appearance of suitable creation tools (often based on game engines) have made easy its expansion to many other fields of application in everyday life (education, health, architecture, marketing and, of course, video games).
MAS integrate a spread of robust AI techniques from different fields, ML provides one of the most productive and solution-generating focuses on the history of science and engineering, while XR (the union of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality) has become a must technology in areas such as information visualisation, video games, simulation, design, and research, offering realistic solutions both from a development and interactive point of view.
Although until a few years ago most of the technological solutions for real-time 3D rendering were based on the use of very specialised low-level libraries (like Ogre, based on OpenGL specifications), nowadays there is remarkable availability of very high-performance software that facilitates the access and creation of high-quality content with a relatively low previous training. Some of the most successful examples in this direction are the result of products that started as video game creation engines (Unity, Unreal Engine, LÖVR, Omniverse, or Godot), many of them with free or even open-source licences, and that have gradually expanded their applications to other areas where the creation of 3D multimedia content is at the core (educational experiences, marketing, digital production, architecture, etc.), with Carla as a demonstration of this trend. In recent months, thanks to webGL specification and WebXR, we are even experiencing a web orientation in high-quality 3D tools, promoting the use of web browsing platforms as the basis for experiences previously reserved for professional products (where ThreeJS has become a benchmark OpenSource project, and Unreal and Unity are moving to provide suitable export tools), also leading to the emergence of standardised protocols for XR immersion.
Hence, the integration between tools providing a high visual quality (enriching the feeling of immersion required for IAI) and tools allowing the application of the latest AI developments, becomes a close task in which the efforts invested in visualisation and representation stages are negligible compared to the other tasks, being able to concentrate our efforts in a real and immersive application of AI. Currently, the combination possibilities are varied and provide a flexible working environment, where the independence between the different modules ensures that the design procedure, modelling and capabilities are more robust and stable.
